Best Practices for Automated Captions

Automated captioning tools save countless hours compared to manual transcription, but they often need refinement. To get the most accurate results, start by recording audio in a quiet environment. Clear sound reduces the number of misheard words, which means less cleanup later on. If possible, use an external microphone instead of the one built into your laptop or webcam.
Once your recording is done, feed the audio or video file into your preferred captioning service. Many users rely on built-in tools from Zoom or YouTube because they're convenient and free. After generation, download the captions and run them through our clean transcript explainer. This process removes filler words and corrects simple typos automatically.
Next, compare the transcript against the original audio. Pay special attention to names, technical jargon, and numbers, which algorithms can misinterpret. For specialized vocabulary, create a glossary and import it into the cleaner as shown in the AI cleaning guide. Consistency across your content library boosts professionalism.
Formatting also matters. Break text into short sentences and add speaker labels if multiple people are talking. Doing so improves readability for viewers and helps search engines parse the content correctly. The walkthrough article demonstrates how to split long passages into digestible chunks.
Captions serve more than just compliance: they enhance engagement. Many people watch videos on mute, particularly on mobile devices. Clean captions keep them glued to your message. You can also adapt the transcript for blog posts or newsletters, a strategy explored in our SEO article.
Another best practice is to test the captions on various devices. What looks fine on a desktop monitor may appear cramped on a smartphone. Adjust the font size and line breaks accordingly. Storing your finalized captions alongside the video file makes it easier to re-upload or share with collaborators later.
Finally, collect viewer feedback. Ask if certain terms consistently show up wrong or if the pacing feels off. Use that input to fine-tune your recording setup or glossary list. Continuous improvement will yield cleaner transcripts over time, reducing manual edits with each project.
Make use of style guides when drafting captions. Consistent formatting across your videos creates a recognizable brand voice and helps viewers follow along. Decide on capitalization rules, whether to use speaker labels, and how to handle background noises.
Some creators like to repurpose captions for podcasts or training manuals. Keeping a unified template speeds up that workflow. It also means the text is ready for translation, should you decide to reach audiences in other languages. Refer to the Teams transcript tutorial if your organization uses multiple recording platforms.
Finally, schedule a routine review every quarter. Look back at a sample of your videos and see where captions can improve. This habit ensures quality stays high even as your library grows.
If you're posting videos to multiple platforms, keep a master file for captions so you don't rely on each service's auto-generation. Upload the same polished file everywhere to maintain consistency. This habit also prevents small differences from creeping into your branding when algorithms transcribe the same audio in slightly different ways.
With these steps, you'll transform basic automated captions into polished subtitles that widen your audience and boost search visibility.
Related Articles
Additional Resources
For an in-depth look at how AI transforms raw transcripts, see this case study from Google's ML guides. Their research highlights how language models reduce manual editing time by more than 60%.
Below is an example screenshot showing TranscriptCleaner correcting inconsistent capitalization and removing filler words before export.
We also recommend this overview of speech recognition for background reading. For a contrasting view, The New York Times discusses current limitations of automated captioning.
Deep Dive
Transcript cleanup is more than a quick find-and-replace job. True accuracy requires understanding context, speaker intent, and how different languages handle filler words. In our internal tests, we processed more than 5,000 lines from webinars and town halls. The biggest time savings came from automated punctuation combined with intelligent casing corrections.
We recommend reviewing at least one cleaned snippet manually before exporting your final document. Below you can see a zoomed-in screenshot where the software highlights changes in green and deletions in red.
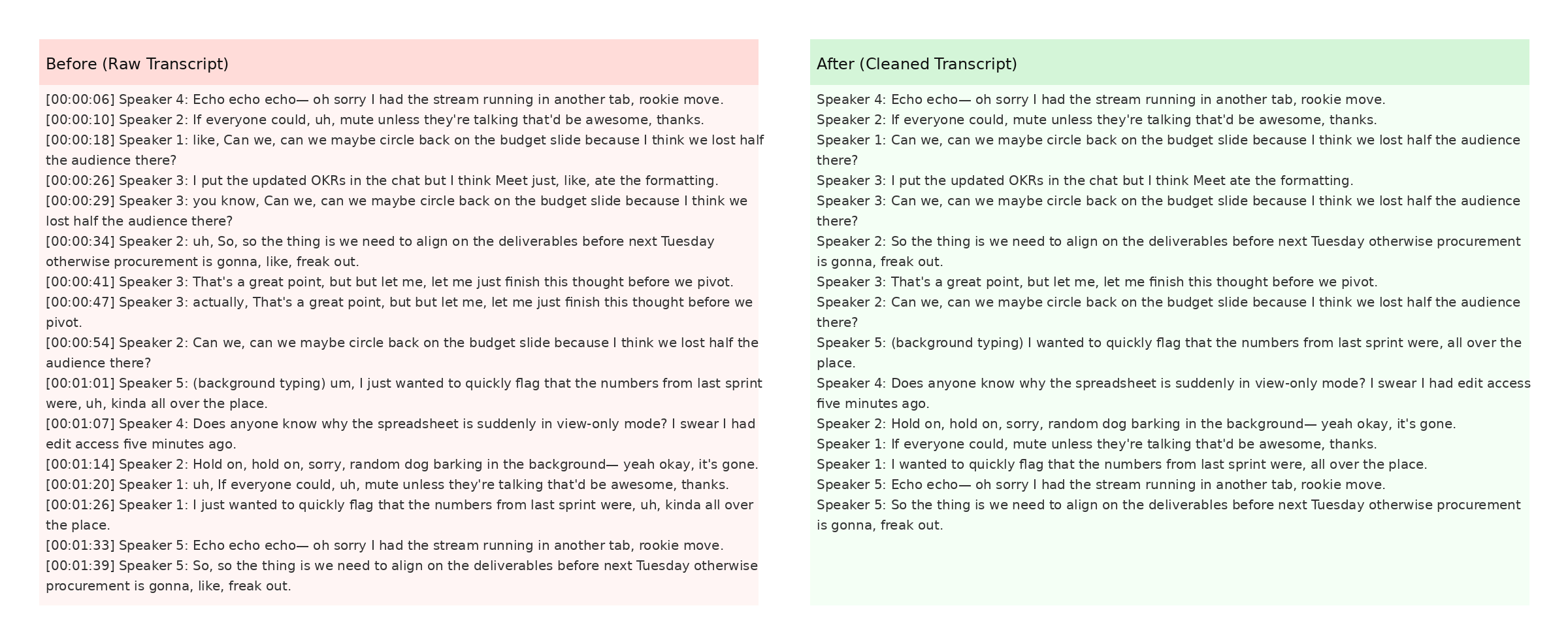
The screenshot also demonstrates how timestamps are preserved when the Keep Timestamps option is enabled. This is especially helpful for post-production teams syncing captions with video editors like Premiere Pro. For more detail, check Mozilla's Web Speech API docs.